1.1 What Is JavaServer Pages?
Put succinctly, JavaServer Pages is a technology for developing web
pages that include dynamic content. Unlike a plain HTML page,
which contains static content that always remains the same, a
JSP page can change its content based on any number of
variable items, including the identity of the user, the user's
browser type, information provided by the user, and selections
made by the user. As you'll see later in the book, this
functionality is key to web applications such as online
shopping and employee directories, as well as for personalized
and internationalized content.
A JSP page contains standard markup language
elements, such as HTML tags, just like a regular web page.
However, a JSP page also contains special JSP elements that
allow the server to insert dynamic content in the page. JSP
elements can be used for a variety of purposes, such as
retrieving information from a database or registering user
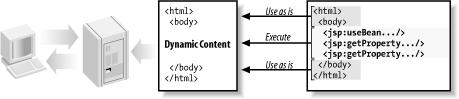
preferences. When a user asks for a JSP page, the server
executes the JSP elements, merges the results with the static
parts of the page, and sends the dynamically composed page
back to the browser, as illustrated in Figure
1-1.
JSP defines a number of standard elements
that are useful for any web application, such as accessing
JavaBeans components, passing control between pages and
sharing information between requests, pages, and users.
Programmers can also extend the JSP syntax by implementing
application-specific elements that perform tasks such as
accessing databases and Enterprise JavaBeans, sending email,
and generating HTML to present application-specific data. One
such set of commonly needed custom elements is defined by a
specification related to the JSP specification: the JSP
Standard Tag Library (JSTL) specification. The combination of
standard elements and custom elements allows for the creation
of powerful web applications. ![]()
|
